How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after, opening doors to stunning aerial photography, efficient inspections, and exciting recreational pursuits. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls, planning effective flight paths, and adhering to crucial safety and legal regulations. We’ll explore both fundamental and advanced techniques, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
From the intricacies of propeller types and flight controller functions to the art of capturing breathtaking aerial footage, we will navigate the world of drone operation with clarity and precision. We’ll cover essential safety protocols, legal considerations, and troubleshooting tips, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable flight experience for both beginners and experienced pilots alike. By the end, you will possess the confidence and expertise needed to utilize your drone responsibly and effectively.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various parts of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the major components and introduce common terminology used in the drone community.
Major Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components working in harmony. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust, speed, and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands. It integrates data from the GPS, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), barometer, and other sensors.
- Battery: The power source for the drone, typically a Lithium Polymer (LiPo) battery. Battery life is a critical factor affecting flight time.
- GPS Module: Provides location data, crucial for autonomous flight modes and features like Return-to-Home (RTH).
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the drone’s orientation and movement, helping the flight controller maintain stability.
- Radio Transmitter (Remote Controller): Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and functions.
- Camera (optional): Many drones are equipped with cameras for capturing aerial photos and videos.
Glossary of Common Drone Terminology
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding and interaction with the drone community.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing image shake.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, such as a camera or other equipment.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor.
- Firmware: The software that controls the drone’s functions.
- LiPo Battery: Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of battery used in drones.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees in real-time.
Drone Propeller Comparison
Different propellers are designed for various flight characteristics. The choice of propeller significantly impacts the drone’s performance.
| Propeller Type | Pitch | Diameter | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slow-pitch | Low | Large | High lift, low speed, longer flight time |
| Fast-pitch | High | Small | High speed, less lift, shorter flight time |
| Standard | Medium | Medium | Balance between lift, speed, and flight time |
| Folding | Variable | Variable | Portability, ease of transport |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safe operating procedures are paramount to ensure a successful and safe flight. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Verify the GPS signal is strong and stable.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU if necessary.
- Check the controller’s battery level.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm that you are in a legal and safe flying area.
Safe Operating Procedures
Maintaining a safe distance from obstacles, people, and property is crucial. Always be aware of your surroundings.
- Keep a safe distance from obstacles (buildings, trees, power lines).
- Avoid flying over crowds or people.
- Never fly near airports or restricted airspace.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Be mindful of wind conditions and avoid flying in strong winds.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Flowchart
A systematic approach to takeoff and landing minimizes risks.
(A visual flowchart would be included here, illustrating the steps: pre-flight checks, power on, motor calibration, gentle ascent, hovering, maneuvering, descent, landing, power off. Each step would be a box in the flowchart with arrows indicating the flow.)
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the controls on your drone’s remote is fundamental to successful operation. This section covers basic maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions
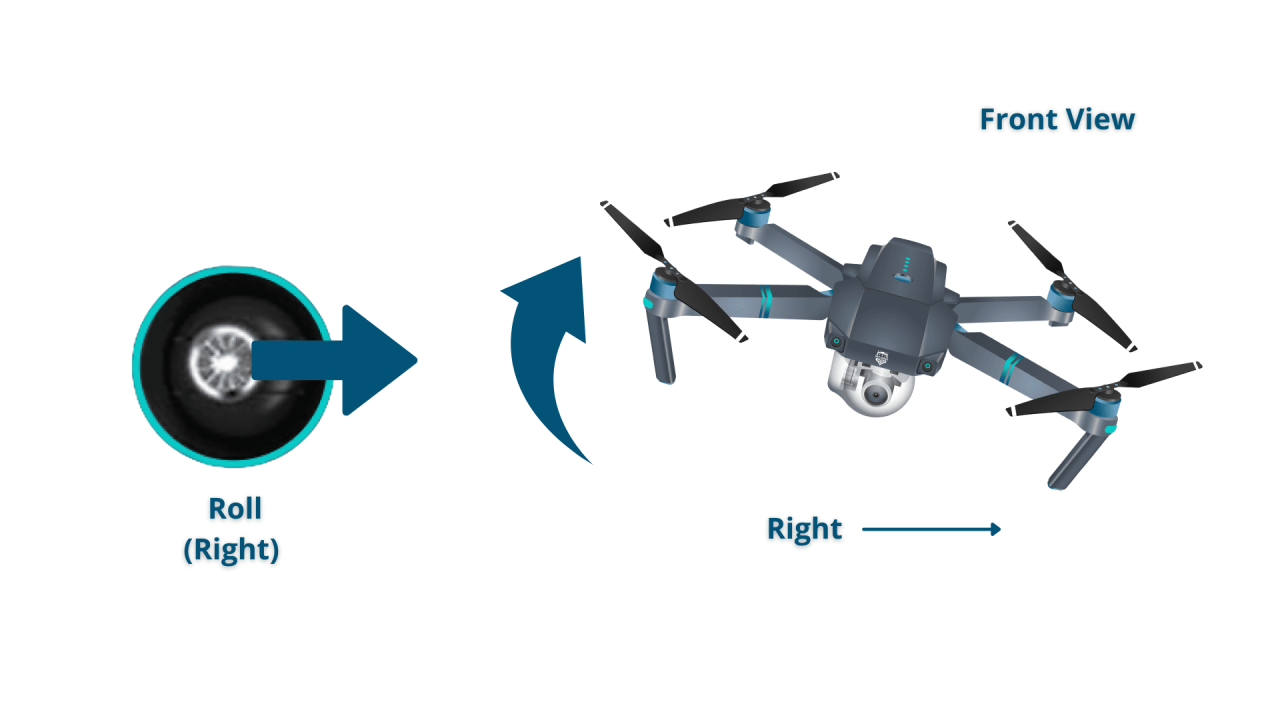
Most drone remotes have two control sticks (or thumbsticks) and several buttons. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls roll (tilt) and pitch (forward/backward movement).
- Left Stick: Altitude (up/down), Yaw (left/right rotation)
- Right Stick: Pitch (forward/backward), Roll (left/right tilt)
- Buttons: These vary depending on the drone model but often include RTH (Return to Home), camera controls, and flight mode selection.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Gently move the left stick upwards to increase altitude.
- Descending: Gently move the left stick downwards to decrease altitude.
- Turning: Use the left stick to rotate the drone left or right.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Use the right stick to move the drone forward or backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Use the right stick to move the drone left or right.
Controlling Altitude and Orientation
Precise control over altitude and orientation is essential for smooth and controlled flights. Practice makes perfect.
Maintaining a steady altitude requires careful manipulation of the left stick. Adjusting the drone’s orientation (roll and pitch) requires precise use of the right stick. Practice in a calm environment to master these skills.
Navigating and Planning Flights

Effective flight planning ensures safe and productive drone operations. This includes understanding GPS navigation and considering various factors.
Using GPS and Waypoint Navigation
Many drones offer GPS-assisted navigation features, allowing for autonomous flights and pre-programmed flight paths. Waypoints are pre-defined locations that the drone will fly to in sequence.
Most drone apps allow you to create waypoints on a map, set the drone’s altitude, and speed for each waypoint. The drone will then autonomously follow the planned path.
Flight Path Planning Strategies
Planning flight paths depends on the objective, whether it’s capturing aerial footage or conducting inspections. Consider factors like camera angle, lighting, and the subject’s position.
- Aerial Photography: Plan a flight path that provides optimal angles and lighting for capturing the desired scene.
- Inspections: Plan a systematic path to cover the entire area needing inspection, ensuring all critical areas are visible.
Factors to Consider When Planning a Drone Flight
Several factors influence flight safety and success.
- Weather Conditions: Wind speed, rain, and visibility significantly impact flight safety.
- Airspace Restrictions: Check for any airspace restrictions or no-fly zones in your area.
- Battery Life: Plan your flight duration considering the battery’s capacity.
- Obstacles: Identify and avoid any potential obstacles in your flight path.
- Legal Requirements: Ensure you comply with all applicable regulations.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring safe operation. This section covers essential maintenance procedures and common troubleshooting steps.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from beginner to intermediate levels, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and improve your skills. This will help ensure safe and responsible drone operation.
Drone Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and inspection are essential to maintain the drone’s performance and longevity.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Proper training and understanding are crucial for responsible and enjoyable drone piloting.
- Clean the propellers: Remove dirt and debris from the propellers using a soft brush.
- Clean the body: Wipe down the drone body with a damp cloth.
- Inspect the motors: Check for any damage or loose parts.
- Inspect the battery: Check for any signs of damage or swelling.
- Inspect the camera: Clean the camera lens with a microfiber cloth.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save time and prevent costly repairs.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Check battery, try a different battery, inspect the power switch |
| Drone is unstable in flight | GPS signal loss, wind, calibration issues | Ensure strong GPS signal, avoid strong winds, recalibrate the IMU and compass |
| Motor failure | Motor damage, ESC failure | Inspect motors and ESCs for damage, consider professional repair |
| Camera malfunction | Camera damage, software issue | Inspect camera for damage, check firmware updates |
Battery Care and Storage
Proper battery care is crucial for safety and longevity. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storage.
- Charge batteries at room temperature.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries.
- Do not leave batteries unattended while charging.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. These vary by location.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Before flying, research and understand the specific regulations in your area. This typically includes registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Many countries and regions require drone registration, limiting flight altitudes, and mandating adherence to specific operational guidelines, including maintaining visual line of sight and avoiding populated areas.
Airspace Restrictions and Permits

Certain areas have restricted airspace, such as airports, military bases, and national parks. Flying in these areas is often prohibited without specific permits or authorization.
Some regions may require permits or licenses for commercial drone operations or flights involving specific activities. Always check with the relevant aviation authorities for information specific to your location and intended use.
Summary of Key Regulations, How to operate a drone
The following table provides a general overview. It is crucial to consult official sources for accurate and up-to-date information specific to your region.
| Regulation | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Drone Registration | Requirement to register your drone with the relevant authority. | Failure to register can result in fines or legal penalties. |
| Airspace Restrictions | Prohibition of flight in certain areas, such as airports and restricted zones. | Flying in restricted airspace can lead to serious consequences. |
| Operational Limitations | Rules governing flight altitude, distance from people, and other operational parameters. | Non-compliance can result in fines or other penalties. |
| Privacy Concerns | Regulations regarding the use of drones to capture images or videos of individuals or private property. | Violating privacy laws can have serious legal repercussions. |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the key components, safety procedures, and flight techniques essential for safe and successful drone operation. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to regulations, and a commitment to safety are paramount. As you progress, explore advanced techniques and always prioritize responsible flight practices.
The skies await – fly safely and responsibly!
General Inquiries
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home features, and beginner modes is recommended. Look for drones with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15-30 minutes, often less in windy conditions or with heavy camera use. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose GPS signal?
Many drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if it loses GPS signal. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone and be prepared to manually control it if necessary.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and registration procedures. Failure to register may result in penalties.
